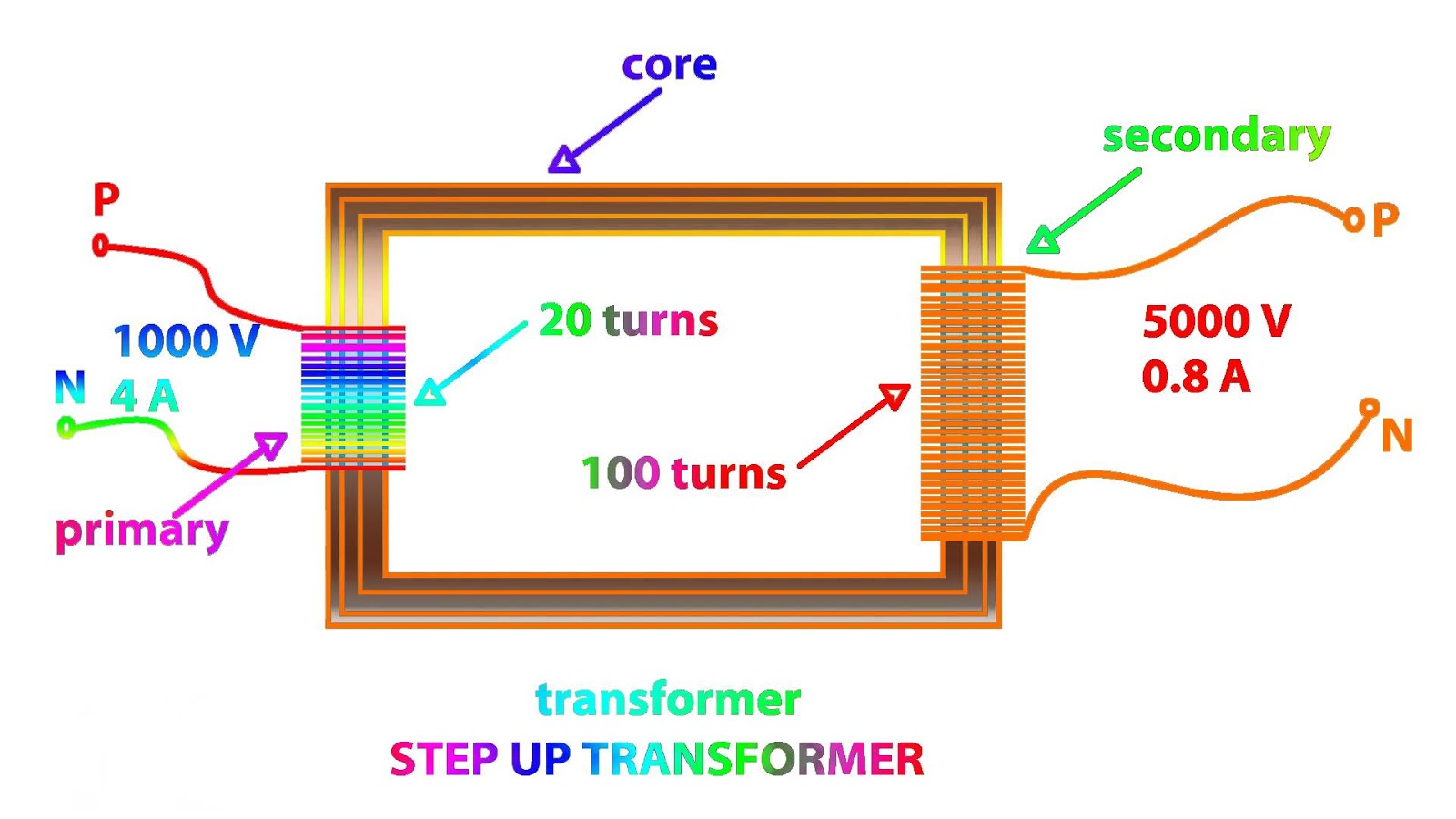
Step Up Transformer
the transformer is static electrical equipment which transforms electrical energy (from primary side windings) to the magnetic energy (in transformer magnetic core) and again to the electrical energy (on these secondary transformer sides). The operating frequency and nominal power are approximately equal on primary and secondary transformer side because the transformer is a very efficient equipment, while the voltages and currents values are usually different. Essentially, that is the main task of the transformer, converting high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current on the secondary side and vice versa. Also, a transformer with its operation principle provides galvanic isolation in the electrical system.
With those features, the transformer is the most important part of the electrical system and provides economical and reliable transmission and distribution of electrical energy. The transformer can transfer energy in both directions, from HV to LV side as well as inversely. That is the reason why it can work as voltage step up or step down transformer. Both transformer types have the same design and construction. Any transformer can operate as step-up or step-down type. It is only depending on the energy flows direction.
The HV windings contain a huge number of turns compared with the LV windings. An LV winding wire has bigger cross-section than HV wire because of higher current value on the LV side. Usually, the LV windings are placed close to the transformer core and over them, the HV windings are wounded.
Transformer turns ratio is approximately proportional to the voltage ratio (U1/U2=N2/N1), where U1,2 are voltages and N1,2 are the turns numbers on HV and LV side). The primary side of a step-up transformer has a small number of turns (LV side) while the transformer secondary side has any numbers of turns (HV side). That means an energy flows from the LV to HV side.
The most important application of step-up transformer is a generator step-up (GSU) transformer which is used in all generating plants. Those transformers usually have large turns ratio value. The voltage value produced in energy generation is increased and prepared to the long distance energy transmission. The energy produced in generating plant is characterized by allowing voltage and high current value. Depending on the generating plant type, the GSU transformer has nominal primary voltage value from 6 up to 20 kV.
The nominal voltage value of GSU secondary side can be 110 kV, 220 kV, 410 kV depending on energy transmission system which is connected to the GSU secondary side. The current value on the primary GSU side is usually very high and depending on the nominal transformer power can reach even 30000 A. This current value is not practical for energy transmission and has to be decreased because of the transmission power losses (R × I2). Long distance energy transmission would not be possible. Besides the GSU transformer also makes galvanic isolation between the generator and electrical network.
Applications of Step Up Transformer
The small step-up transformers can be used in electronic and electrical devices where the voltage boosting is required. But nowadays in the modern electronic device, power electronic circuits are more frequently used because of weight and dimension.
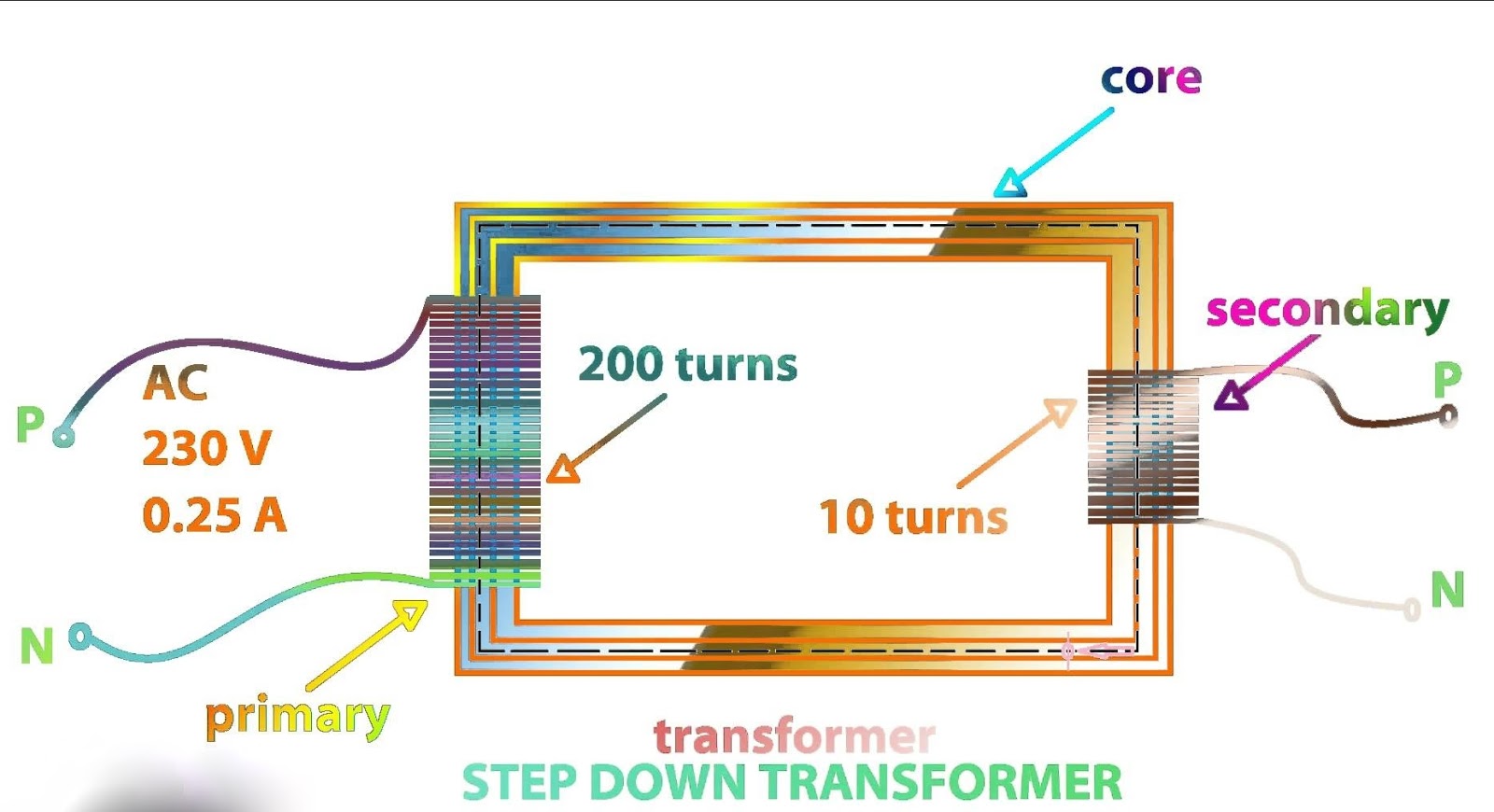
Step Down Transformer
The step-down transformer converts the high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current value on the secondary side. This transformer type has a wide application in electronic devices and electrical systems. When it comes to the operation voltage, the step-up transformer application can be roughly divided into two groups: LV (voltages up to 1 kV) and HV application (voltages above 1 kV). The first LV application refers to the transformers in electronic devices. Supplying the electronic circuits requires a low voltage value (e.g. 5V, even lower values nowadays).
The step-down transformer is used to provide this low voltage value which is suitable for electronics supplying. It transforms home voltage (230/120 V) from primary to a low voltage on the secondary side which is used for the electronic supplying. If electronic devices are designed to have higher nominal power, transformers with high operating frequency are used (kHz-s). The transformers with higher nominal power value and 50/60 Hz nominal frequency would be too large and heavy. Also, the daily used battery chargers use the step-down transformer in its design.
The step-down transformers have a very important function in power system. They lower the voltage level and adapt it for energy consumers. It is performed in several steps described below:
- A long-distance energy transmission system should have voltage level as high as possible. With high voltage and low current, the transmission power loss
will be significantly decreased. A power grid is designed that has to be connected to the transmission system with the different voltage levels. Step-down transformers are used in the interconnection of transmission systems with different voltage level. They decrease voltage level from high to lower value (e.g. 765/220 kV, 410/220 kV, 220/ 110 kV). These transformers are huge and have very high nominal power (even 1000 MVA). In this case, when the transformer turns ratio is not high the autotransformers are usually installed.
- The next voltage level transformation step is adapting transmission voltage to the distribution level. The characteristic voltage ratios in this case are 220/20 kV, 110/20 kV (also the LV secondary voltages 35 kV and 10 kV can be found). The nominal power of those transformers is up to 60 MVA (usually 20 MVA). The on-load tap changer is almost always installed in these transformers. A voltage regulation is the main function of tap changer. In USA the tap changer is based on LV side, and in rest of the world mostly on the HV transformer side.
- The final voltage transformation step is adapting the voltage to the home voltage level
. These transformers are known as small distribution transformers with nominal power up to 5 MVA (mostly below of 1 MVA) and with nominal voltage values 35, 20, 10 kV on HV side and 400/200 V on LV side. It is noticeable that those transformers have high turns ratio. They usually have de-energized tap changer with 5 tap position (+/- 2 tap position) and do not have on load tap changer..