The automotive industry has seen significant advancements in recent years, and one of the key innovations in vehicle steering technology is the electric power steering (EPS) system. Unlike traditional hydraulic power steering, which relies on fluid pressure, the electric power steering system utilizes an electric motor to provide steering assistance. This article will delve into the intricacies of the electric power steering system, exploring its working principles, advantages, components, challenges, and future trends.

Table of Contents
What Is Electric Power Steering System?
The electric power steering (EPS) system is a modern steering technology that has gained popularity due to its numerous benefits over conventional systems. It replaces the hydraulic power assist mechanism with an electric motor, resulting in a more efficient and precise steering experience. By eliminating the need for a hydraulic pump, belts, and hoses, the electric power steering system offers a simpler and lighter solution.
Components of Electric Power Steering
The Electric Power Steering system comprises several key components that work together to ensure smooth and responsive steering. These components include:
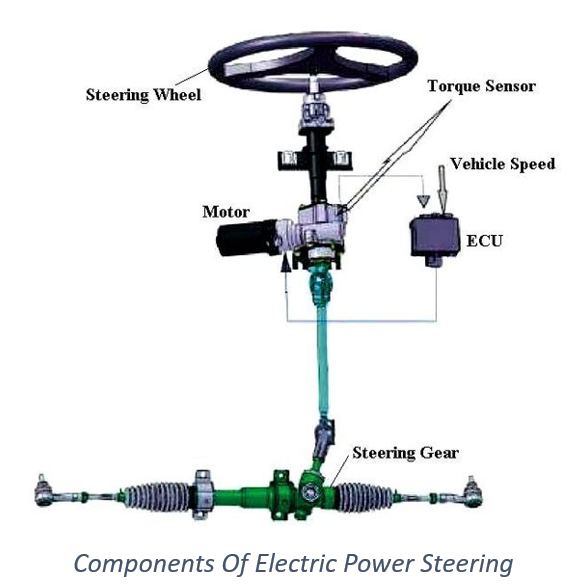
Electric Motor
The electric motor is the primary component of the EPS system. It is responsible for generating the necessary torque to assist with steering. The motor is usually mounted either on the steering column or on the steering rack.
Electric Control Unit
The control unit, often referred to as the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), manages the overall operation of the EPS system. It receives input signals from various sensors and calculates the appropriate amount of power assistance required based on factors such as steering wheel position, vehicle speed, and driver inputs.
Torque Sensor
The torque sensor measures the amount of force applied to the steering wheel by the driver. It provides feedback to the control unit, allowing it to adjust the assistance level accordingly. This sensor helps ensure that the power assistance is proportional to the driver’s steering inputs.
Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor detects the position of the steering wheel and the angle at which it is turned. This information is used by the control unit to determine the appropriate level of assistance required during different driving conditions.
Speed Sensor
The speed sensor monitors the vehicle’s speed and provides input to the control unit. It helps the system adjust the level of power assistance based on the vehicle’s velocity. At higher speeds, less assistance is typically needed.
Wiring and Connectors
The EPS system consists of various wiring harnesses and connectors that interconnect the different components. These ensure the proper transmission of electrical signals between the control unit, sensors, and the electric motor.
Steering Column
The steering column connects the steering wheel to the steering gear. It allows the driver to turn the wheels by transmitting the rotational movement from the steering wheel to the rest of the steering system.
Steering Gear
The steering gear, also known as the rack-and-pinion mechanism, converts the rotational movement from the steering column into the linear motion required to turn the vehicle’s wheels.
Types of Electric Power Steering Systems
There are two main types of electric power steering systems: column-mounted EPS and rack-mounted EPS.
Column-Mounted Electric Power Steering
In column-mounted EPS, the electric motor is located on the steering column itself. This design simplifies installation and allows for retrofitting in existing vehicles. Column-mounted EPS is commonly found in smaller cars and compact vehicles.
Rack-Mounted Electric Power Steering
Rack-mounted EPS, as the name suggests, places the electric motor directly on the steering rack. This design offers greater steering precision and is commonly used in larger vehicles and performance cars. Rack-mounted EPS provides a more direct steering feel and better road feedback.
How Does Electric Power Steering Work?
The working principle of electric power steering involves a series of steps that seamlessly translate the driver’s input into a controlled movement of the wheels. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Sensor Signals
As the driver turns the steering wheel, sensors in the electric power assist system detect the rotational movement and send corresponding signals to the electronic control unit (ECU). These signals provide crucial information about the driver’s steering input.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The electronic control unit (ECU) receives the sensor signals and analyzes them to determine the appropriate level of steering assistance needed. The ECU takes into account factors such as the vehicle’s speed, the angle of the steering wheel, and the driving conditions to calculate the optimal level of assistance.
Electric Motor
Based on the inputs received from the ECU, the electric motor provides the necessary assistance by applying torque to the steering gear. The torque generated by the motor assists the driver in turning the wheels with minimal effort.
Advantages of Electric Power Steering
Electric power steering offers several benefits over traditional hydraulic systems. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Improved Fuel Efficiency
EPS consumes less power compared to hydraulic systems, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. By eliminating the need for a hydraulic pump constantly driven by the engine, EPS reduces the load on the engine, thus increasing overall fuel economy.
Enhanced Control and Responsiveness
Electric power steering provides precise control and responsiveness, allowing drivers to navigate with ease. The assistance provided by EPS can be adjusted based on driving conditions, vehicle speed, and driver preferences, resulting in a personalized driving experience.
Reduced Maintenance
Since EPS does not rely on hydraulic fluid, there is no need for periodic fluid checks, leak repairs, or pump replacements. This leads to reduced maintenance costs and ensures a more reliable steering system.
Flexibility in Design
Electric power steering systems offer greater flexibility in design and integration. They can be easily integrated with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and enable features like lane-keeping assist and parking assist. EPS also allows for more compact packaging, creating additional space in the engine compartment.
Disadvantages of Electric Power Steering
While electric power steering (EPS) systems offer numerous advantages, there are also a few disadvantages to consider. It’s important to weigh these drawbacks against the benefits when evaluating the suitability of EPS for a particular application. Here are some of the key disadvantages:
Lack of Mechanical Feedback
One of the primary concerns with EPS is the reduced mechanical feedback compared to hydraulic systems. Hydraulic power steering provides a direct connection between the steering wheel and the road, allowing drivers to feel the road surface and make more precise adjustments. With electric power steering, the feedback is often filtered or simulated electronically, which can result in a somewhat artificial steering feel.
Reliance on Electrical Power
Electric power steering systems are entirely dependent on electrical power to function. In the event of an electrical system failure or power loss, the steering assistance may be compromised or completely disabled. While modern EPS systems have fail-safe mechanisms to allow for manual steering, the reliance on electrical components introduces a potential vulnerability.
Cost and Complexity
Compared to hydraulic power steering, electric power steering systems can be more expensive to manufacture and maintain. The inclusion of electrical components, such as motors, sensors, and control units, increases the complexity and cost of the system. In case of a malfunction or failure, the repair or replacement of these components can be more costly.
Sensitivity to Electrical Issues
Electric power steering systems are sensitive to electrical disturbances or issues within the vehicle’s electrical system. Voltage fluctuations or wiring problems can potentially affect the performance and reliability of the EPS system. It’s important to ensure proper electrical grounding and maintain the integrity of the electrical connections to mitigate these risks.
Limited Assistance in Manual Mode
In situations where the EPS system fails or switches to manual modes, such as during electrical failures, the steering assistance is significantly reduced. This can make steering more difficult, especially at low speeds or when parking. Drivers may need to exert more effort to steer the vehicle, which can be challenging for some individuals, particularly those with physical limitations.
Benefits of Electric Power Steering
Electric power steering systems offer several benefits that contribute to a superior driving experience.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
One of the significant advantages of electric power steering is improved fuel efficiency. Since EPS does not rely on a hydraulic pump, it eliminates the constant power drain associated with hydraulic systems. This results in better overall fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Enhanced Steering Response
EPS provides more precise control and better feedback compared to hydraulic systems. The electric motor can adjust the level of assistance based on driving conditions, resulting in improved handling and manoeuvrability. The driver can experience a more connected and responsive steering feel.
Variable Steering Assist
Electric power steering allows for variable steering assist, meaning the level of assistance can be adjusted according to the driving situation. At higher speeds, less assistance is required, providing a firmer and more stable steering feel. At lower speeds, more assistance is provided, making parking and manoeuvring easier.
Reduced Maintenance
The electric power steering system requires less maintenance compared to traditional hydraulic power steering systems. There are no fluids to change, no belts to replace, and fewer moving parts that can wear out over time. This leads to reduced maintenance costs and a more reliable steering system.
Conclusion
The electric power steering system has revolutionized the way vehicles are steered. With its numerous advantages over traditional hydraulic systems, it provides a more efficient, precise, and enjoyable driving experience. As technology advances and further innovations are made, EPS will continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of automotive steering systems.
FAQs
Is electric power steering better than hydraulic power steering?
EPS offers several advantages over hydraulic power steering, including improved fuel efficiency, precise control, and variable steering assist. However, the choice between the two depends on individual preferences and specific vehicle requirements.
Can electric power steering fail?
While EPS systems are generally reliable, like any other electronic system, they can experience malfunctions or failures. However, modern systems are designed with fail-safe mechanisms to ensure continued steering functionality in case of electrical issues.
Do electric power steering systems require regular maintenance?
EPS systems require less maintenance compared to hydraulic systems. There are no fluids to change or belts to replace. However, periodic inspections and diagnostics are recommended to ensure optimal performance and detect any potential issues.
How does electric power steering improve fuel efficiency?
EPS improves fuel efficiency by eliminating the constant power drain of a hydraulic pump. Since EPS does not rely on hydraulic fluid, it reduces the energy required to operate the steering system, resulting in improved overall fuel economy.
Are there any safety concerns with electric power steering?
EPS systems are designed with safety in mind and undergo rigorous testing to meet industry standards. However, as with any automotive system, it is important to ensure regular maintenance and inspections to detect and address any potential safety concerns. If you notice any unusual behaviour or experience difficulties in steering, have the system inspected by a qualified professional.






