Have you ever questioned who invented the mobile phone? It is impossible to imagine a world without mobile phones because they have become such an essential part of our everyday life. Have you ever questioned who invented the mobile phone? These devices have revolutionised the way we work and access information, but have you ever thought about who invented them?
The history of mobile phones is a fascinating one that has been distinguished by a large number of breakthroughs and inventions that have prepared the way for the modern Smartphone that we use today. Although there is no one person who is given credit for developing the mobile phone, the narrative of how it was developed is one of teamwork involving a large number of exceptionally skilled scientists and engineers.
We’re going to take a look at the history of mobile phones and see how they’ve progressed over the years, from the first bulky and pricey devices to the sleek and powerful smartphones that we use today.
This blog article will take you on an amazing voyage through the interesting history of mobile phones. It doesn’t matter if you’re a history buff, a fan of technology, or simply interested in the innovation that altered the world; this post will take you there.
Table of Contents
Who invented the mobile phone?

Martin Cooper, a Motorola engineer, made the first hand-held phone that could connect through Bell’s AMPS. In 1984, Motorola came out with DynaTAC. It was called “The Brick” and weighed more than a kilogramme, but it quickly became a must-have item for wealthy financiers and business owners.
About Martin Cooper
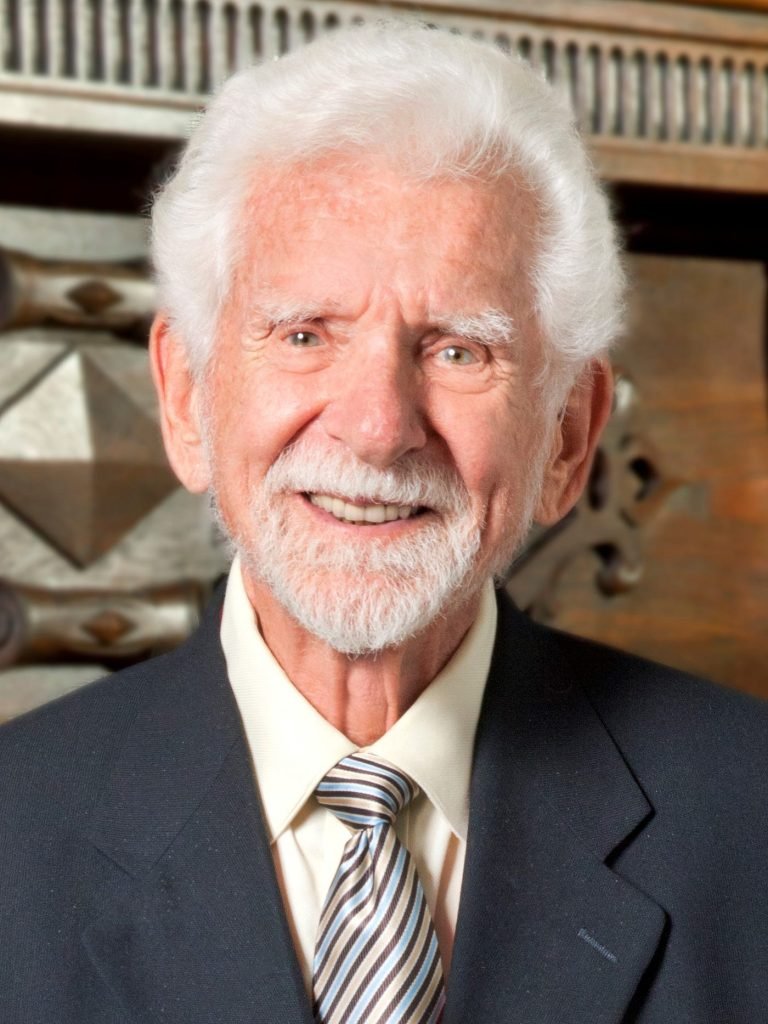

In 1972 and 1973, American engineer Martin Cooper, better known by his nickname, Marty Cooper created and made the world’s first mobile cell phone call. He was born on December 26, 1928, in Chicago, Illinois. It is generally agreed that he invented the first mobile phone.
Cooper has a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from Chicago’s Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) (1950). In the midst of the Korean War, he enlisted in the United States Navy. He worked for the Teletype Corporation after World War II and then for Motorola beginning in 1954. From IIT he graduated with a master’s in electrical engineering (1957). Cooper developed the first radio-controlled traffic-light system in 1960 and oversaw the introduction of the first handheld police radios in 1967 while at Motorola, where he worked on numerous projects involving wireless communications. After that, from 1978 to 1983, he was the company’s vice president and director of R&D.
History of mobile phone
The first mobile phone was created in 1947 by a group of engineers at Bell Labs, however, the history of mobile phones dates back to the middle of the 20th century. The gadget was big and bulky because it was meant to be used in automobiles. Calls were sent and received by radio waves, but the technology was not generally available.
The first portable cellular phone did not appear until the 1970s. The first-ever public call made using a handheld mobile phone (a Motorola DynaTAC 8000X) was made by Motorola developer Martin Cooper in 1973. The equipment weighed about 2.5 pounds and set you back $3,995, which is equivalent to about $10,000 in today’s money.
It wasn’t until the 1980s that mobile phones became mainstream, but even then they were pricey and cumbersome. The Motorola DynaTAC 8000X was the world’s first commercially available mobile phone when it debuted in 1983. Though cumbersome and unwieldy, this gadget opened the way for smaller, lighter mobile phones.
When more compact and inexpensive mobile phones became available in the 1990s, the market for them exploded. As a result, rivalry rose among producers, and they began putting more emphasis on improving mobile phones’ features and capabilities. IBM’s Simon smartphone from 1992 was the first of its kind; it included a touch screen and could send and receive faxes and emails.
With the release of the BlackBerry in 2002 and the iPhone in 2007, the smartphone market exploded in the 2000s. These gadgets were more compact, had more processing power, and had many more capabilities than just making and receiving phone calls and text messages. As a result, they significantly altered the ways in which people obtained and shared information.
There are now billions of people all around the world who use mobile phones, making them an essential part of our daily lives. They have become indispensable in many facets of modern life, having revolutionized how we interact with one another, perform our jobs, and gain access to information. It’s exciting to think about what the future of mobile technology may hold, and the history of mobile phones is intriguing.
The future of mobile communication
The future of mobile communication is an exciting and rapidly evolving landscape, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for connectivity. Several key trends are shaping the future of mobile communication, including the development of 5G and beyond, the integration of mobile phones in a connected world, the emergence of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, and the ethical considerations surrounding convenience and privacy.
- 5G and Beyond:
- The next generation of mobile connectivity The rollout of 5G networks is well underway, offering significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity compared to previous generations. With 5G, mobile communication will enable faster download and upload speeds, seamless streaming of high-quality multimedia content, and support for emerging technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) devices. Beyond 5G, research and development efforts are already exploring even more advanced technologies such as 6G, which could unlock further improvements in speed, latency, and connectivity.
- Innovation and integration:
- Mobile phones in a connected world Mobile phones have become an integral part of our lives, serving as our primary means of communication, information access, and entertainment. In the future, mobile phones will continue to evolve and integrate with other aspects of our lives. They will become more than just devices for communication, incorporating advanced features such as biometric authentication, AI-powered assistants, and seamless integration with other smart devices, including wearables, smart homes, and connected cars.
- Emerging technologies:
- Virtual reality, augmented reality, and the mobile phone Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are rapidly advancing technologies that have the potential to transform mobile communication. Mobile phones, with their high-resolution displays and processing power, are becoming the primary platforms for VR and AR experiences. In the future, we can expect more immersive and interactive mobile applications, games, and experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. These technologies will revolutionize fields such as gaming, education, healthcare, remote collaboration, and more.
- Ethical considerations:
- Balancing Convenience and Privacy in the Age of Mobile Communication As mobile communication continues to advance, ethical considerations surrounding privacy and data security become increasingly important. Striking a balance between convenience and privacy will be crucial. It will require robust data protection measures, transparent privacy policies, and user consent mechanisms. Additionally, the responsible use of emerging technologies like facial recognition, location tracking, and data collection will be essential to ensure that individual’s privacy rights are respected.
Overall, the future of mobile communication holds immense potential for innovation and transformation. With the advent of technologies like 5G, VR, and AR, mobile phones will become even more powerful and integrated into our daily lives. However, it is important to address ethical considerations and prioritize user privacy to build a future where convenience and connectivity coexist harmoniously.