
Hydraulic pumps are the backbone of hydraulic systems, powering everything from simple hand tools to heavy-duty machinery. Understanding the different types of pumps available and their specific advantages can help you choose the right pump for your application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
In this article, we have explored the six most common types of hydraulic pumps: gear pump, vane pump, piston pump, screw pump, clutch pump and refuse pump. Each of these pumps has its own unique design, operating principles, and performance characteristics, making them suitable for different applications.
Table of Contents
1. Gear Pump
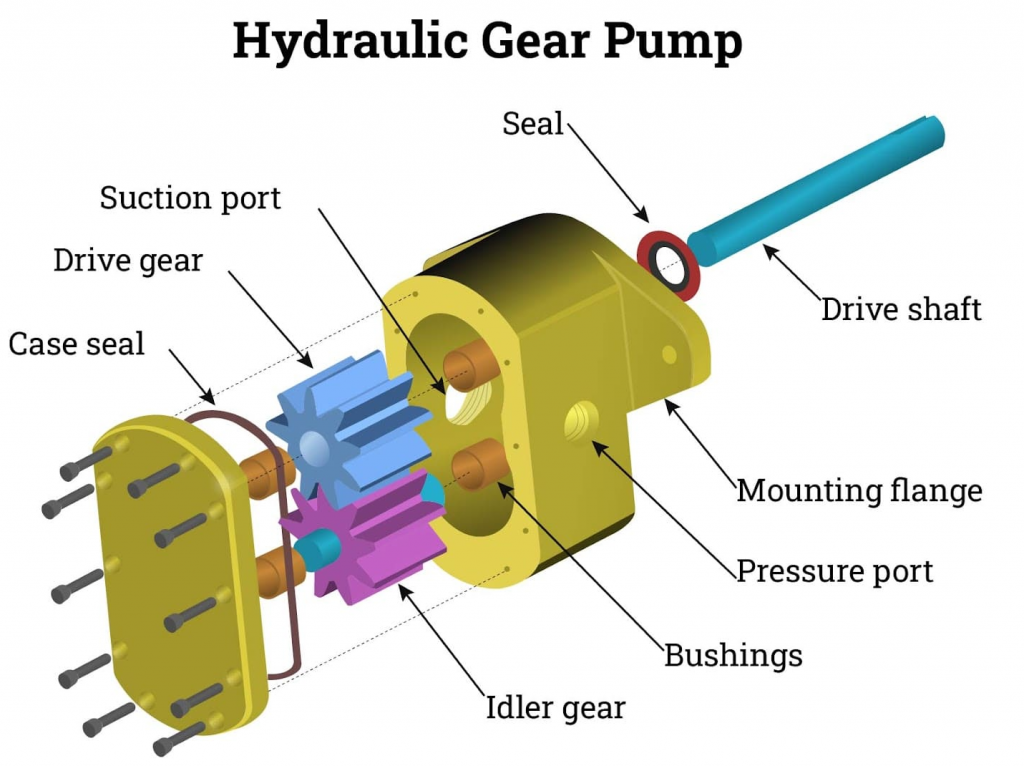
Gear pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that consists of two intermeshing gears that rotate in opposite directions. As the gears turn, they create a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump. As the gears mesh, they force the fluid out of the pump and into the hydraulic system.
Gear pumps are known for their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for many hydraulic applications. They are capable of producing high flow rates at low pressures, making them ideal for applications where high-speed operation is required, such as in hydraulic power steering systems.
One of the advantages of gear pumps is their compact size, which makes them easy to install and maintain. They are also relatively inexpensive compared to other types of hydraulic pumps, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
However, gear pumps do have some limitations. They are not suitable for high-pressure applications, as they are not capable of producing the high pressures required for heavy-duty machinery and equipment. They are also prone to leakage, as the close tolerances required for proper gear meshing can result in fluid bypassing the gears and leaking out of the pump.
Gear pumps are a popular choice for low-pressure hydraulic applications that require high flow rates and compact size. While they do have some limitations, they are reliable, cost-effective, and easy to install and maintain, making them an ideal choice for many hydraulic systems.
2. Vane pump

Vane pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that use a set of vanes mounted on a rotor to create suction and draw fluid into the pump. As the rotor turns, the vanes slide in and out of slots in the pump’s housing, compressing the fluid and forcing it out of the pump.
Vane pumps are known for their efficiency and versatility, as they can handle a wide range of viscosities and produce high flow rates at moderate pressures. They are also relatively quiet and produce less heat than other types of hydraulic pumps, making them an ideal choice for applications where noise and heat generation are a concern.
One of the advantages of vane pumps is their ability to operate at low speeds without sacrificing performance. They are also capable of handling moderate to high pressures, making them suitable for a wide range of hydraulic applications, including hydraulic power steering systems and industrial machinery.
However, vane pumps can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps. They are also prone to wear and can require more frequent maintenance than other types of pumps.
Vane pumps are a versatile and efficient choice for hydraulic applications that require moderate pressure and high flow rates. While they can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps, they offer several advantages, including quiet operation and lower heat generation.
3. Piston pumps
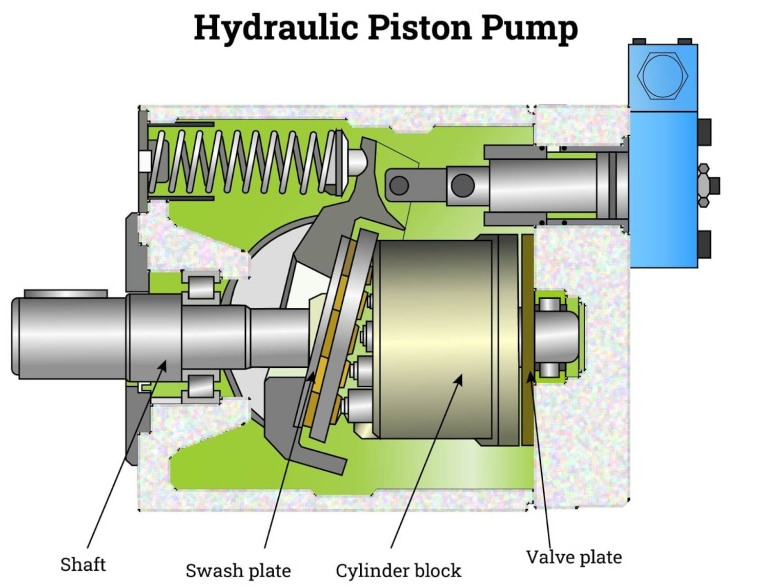
Piston pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that uses a piston and cylinder to generate pressure and move fluid through the system. As the piston moves back and forth in the cylinder, it creates pressure that forces the fluid out of the pump and into the hydraulic system.
Piston pumps are known for their ability to produce high pressure, making them an ideal choice for heavy-duty hydraulic applications, such as construction and mining equipment. They are also highly efficient, producing high flow rates with minimal energy loss.
One of the advantages of piston pumps is their ability to operate at high pressures and handle heavy loads. They are also highly reliable and can provide long service life with minimal maintenance.
However, piston pumps can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps. They also produce more heat and noise than other types of pumps, which can be a concern in some applications.
Piston pumps are a powerful and efficient choice for hydraulic applications that require high pressure and heavy loads. While they can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps, they offer several advantages, including high reliability and long service life.
4. Screw pump
Screw pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that use two interlocking screws to move fluid through the system. As the screws turn, they create a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump. As the screws mesh, they force the fluid out of the pump and into the hydraulic system.
Screw pumps are known for their high efficiency, as they can handle a wide range of viscosities and produce high flow rates with minimal energy loss. They are also highly reliable and can provide long service life with minimal maintenance.
One of the advantages of screw pumps is their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities, making them suitable for a wide range of hydraulic applications, including those that require high pressure and high flow rates. They are also relatively quiet and produce less heat than other types of hydraulic pumps, making them an ideal choice for applications where noise and heat generation are a concern.
However, screw pumps can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps. They are also prone to wear and can require more frequent maintenance than other types of pumps.
Screw pumps are an efficient and reliable choice for hydraulic applications that require high flow rates and a wide range of viscosities. While they can be more complex and expensive than other types of hydraulic pumps, they offer several advantages, including high efficiency and quiet operation.
5. Clutch pump
Clutch pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that are driven by the engine of a vehicle or machine. They are typically used in vehicles and equipment that do not have a dedicated hydraulic system, such as pickup trucks, vans, and agricultural machinery.
Clutch pumps are designed to be compact and easy to install, with a pulley that mounts to the engine and a clutch that engages and disengages the pump. When the clutch is engaged, the pump draws fluid into the system and powers the hydraulic functions of the vehicle or machine.
One of the advantages of clutch pumps is their versatility, as they can be used in a wide range of vehicles and equipment. They are also easy to install and maintain, with minimal additional components required.
However, clutch pumps have some limitations. They are not suitable for high-pressure or high-flow applications, as they are limited by the capacity of the engine. They can also generate additional heat and noise, which can be a concern in some applications.
Clutch pumps are a versatile and cost-effective choice for hydraulic applications in vehicles and equipment without a dedicated hydraulic system. While they have some limitations, they offer several advantages, including ease of installation and maintenance.
6. Refuse Pump
Refuse pumps are a type of hydraulic pump that is used in garbage trucks and other refuse collection vehicles to power the hydraulic system that operates the lifting and dumping mechanisms of the vehicle.
Refuse pumps are designed to handle heavy loads and high-pressure applications, as they must lift and move heavy loads of garbage and debris. They are typically piston pumps, which can provide the high pressure required for this type of application.
One of the advantages of refuse pumps is their durability and reliability, as they must operate in demanding environments and handle heavy loads on a daily basis. They are also designed to be easy to maintain, with simple components and easy access for servicing and repair.
However, refuse pumps can also be prone to wear and damage from debris and other contaminants that are present in the refuse being collected. Regular maintenance and cleaning are important to ensure the longevity and performance of the pump.
Refuse pumps are a critical component of the hydraulic system in garbage trucks and other refuse collection vehicles. They are designed to handle heavy loads and high-pressure applications and are known for their durability and reliability. However, regular maintenance and cleaning are important to ensure their performance and longevity.





